Custom Function Implementation for FileMaker Native Barcode Generator
Buy License Download Demo Support
Tutorial
This tutorial is for the linear version of the Native Generator product, a set of FileMaker Custom Functions that generate barcodes in form and report fields from an already installed system font. This product uses patented Unicode Image technology and is compatible with FileMaker 12 & up on Windows, Mac, and iOS.
Native Generator Custom Functions are only provided for:
- Codabar
- Code 128
- Code 39
- Code 93
- GS1-128
- ITF (Interleaved 2 of 5)
- MSI
All other versions of the Native Generator should refer to the Object Implementation User Manual. Other symbologies cannot be provided as custom functions because of code limitations.
Portions of this product utilize IDAutomation Patent 7,637,436. Databases containing this object may only be distributed outside the licensed organization by purchasing a Developer License.
- Extract the files from the Native Barcode Generator package. Products for this tutorial are located in the "Custom Function Implementation" folder of the compressed file.
-
Start FileMaker Pro Advanced. The advanced version is necessary to embed the
custom functions in the database.
Open the database to generate the barcode and choose File - Manage
Custom Functions. (How
to enable Advanced Features beginning with version FileMaker 17.)
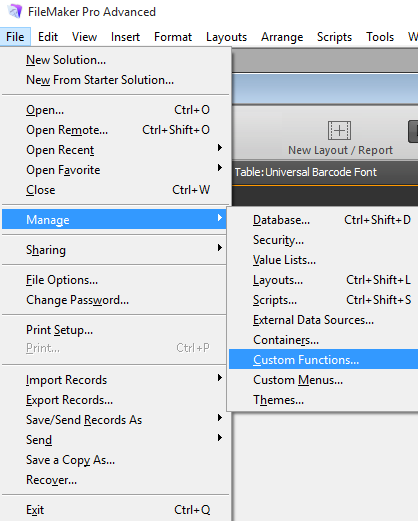
- Choose Import and then select the FileMaker database file that was extracted in Step 1.
-
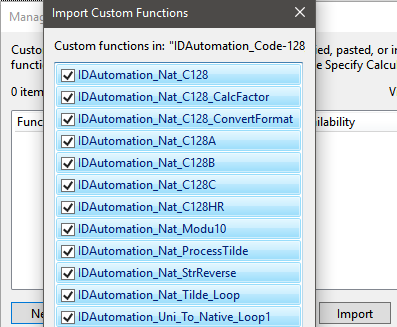
Select one function, then press Ctrl-A and the space bar to
select the remaining functions. It is necessary to
import
all of the functions from the database because several of the functions depend on others to be present.
Note: Failure to
import all functions in this step will result in empty fields instead of
barcodes.
-
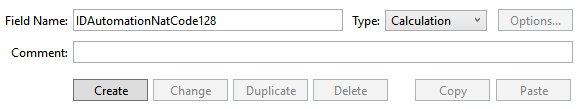
Choose File - Manage - Database to create a calculated field that will contain the
generated barcode.
Name the field to be the same as the related function name, without the
underscores. In this example, the field will be named
IDAutomationNatCode128 and it will call the
IDAutomation_Nat_Code128 function. For the field type, choose Calculation and choose Create.
-
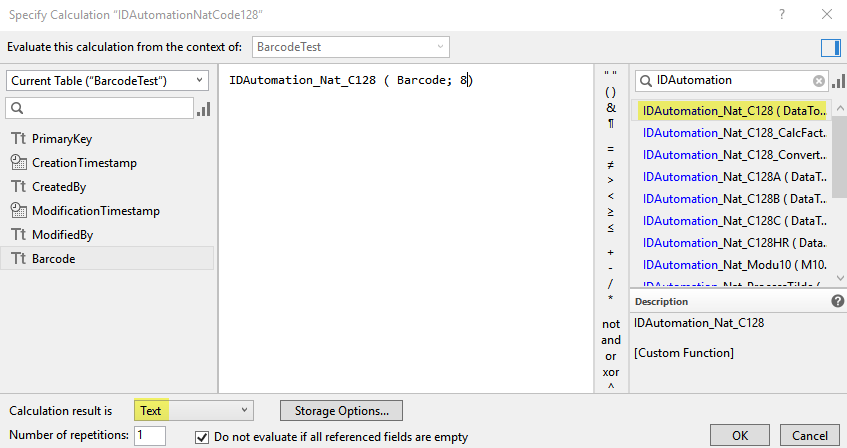
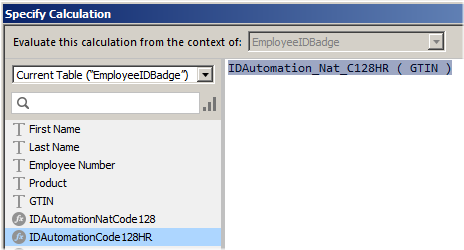
In the specify calculation dialog, change the calculation result to text, choose the
appropriate function from the list on the right, and replace DataToEncode
with the field that needs to be encoded in the barcode and enter a number for
BarHeight such as "8" that determines the height of the barcode.
Optional: The DataToEncode parameter may be changed to a formula that appends text to a field or combines multiple fields. For example:
IDAutomation_Nat_C128( "PREFIX" & Field1 ) or IDAutomation_Nat_C128( Field1 & "," & Field2 ) - Open the FileMaker database file that was extracted in Step 1. Change to
Layout Mode, copy the example barcode field to the clipboard, and paste it into
the database that will generate the barcode.
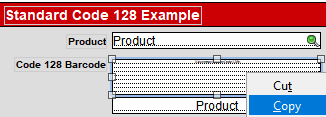
- Right-click on this field and choose Specify Field; choose the calculated
field created in Step 5, in this case, it is
IDAutomationNatCode128.
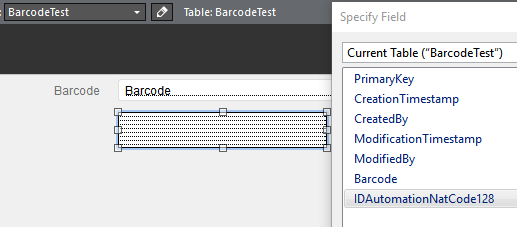
- Size the field so it will completely contain the desired barcode.
- Click on the field and
open the Inspector Window, by going to View -
Inspectors - Inspector:
- In the Appearance section, verify the font selected is a mono-spaced system font such as Courier New, Lucida Console, or Consolas, and the Font Size is 4 points. Note: Courier New is the preferred font to use for linear barcodes and Consolas is the preferred font to use for 2D Matrix barcodes.
- In the paragraph section verify the Line Spacing Height is a height of 0.99. If the barcodes will be displayed on mobile devices with FileMaker Go, set the Line Spacing Height to .95 to reduce horizontal white lines that could appear in the barcode.
-
Verify the Alignment is centered so that an appropriate amount of
white space appears around that barcode.
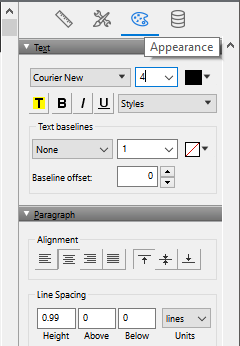
The default point size of 4 generates a barcode X dimension at 16 mils in size. If it is necessary, the point size may be changed according to the following chart.
Note: If the font drop-down box does not contain small sizes, the size must be manually typed in.Point Size Approximate X Dimension 2 08 Mils 3 12 Mils 4 16 Mils 5 20 Mils 6 24 Mils 7 28 Mils 8 32 Mils
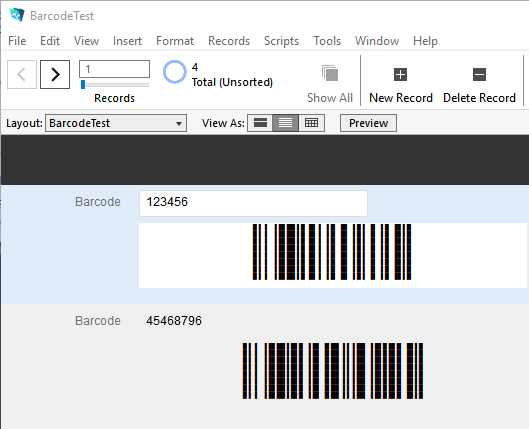
- Optional: If a text interpretation of the barcode is needed, it is suggested to place the appropriate field directly above or below the field that will contain the barcode. To automatically generate the human-readable field for GS1-128, create another calculated field as noted in step 5
with the IDAutomation_Nat_Code128HR function.
- Save and view the form or report. Verify that the barcode symbol is being generated properly on all devices. In some cases, horizontal lines may appear in the barcode because of low screen resolution. However, the printed barcodes should be accurate without any visible lines. An adjustment to the
line spacing property mentioned in Step 10 should
resolve horizontal line issues. If a scanner
is needed to verify printed barcodes, IDAutomation offers several
affordable USB barcode
scanners.


Creating GS1-128 Symbols
IDAutomation includes the capability in this product to create barcodes and HR text for GS1-128 (UCC/EAN128) symbols with the built-in ApplyTilde feature which is enabled by default. The following describes the changes required to implement GS1-128. This GS1-128 symbol example is created from 18 digits of numbers in the GS1DataField field.
- Add in the
application identifiers with
tilde commands. The
result line should be similar to the following:
IDAutomation_Nat_C128( "~202" & GS1DataField )
- If it is desired to place parenthesis in the correct locations of
the text interpretation, the IDAutomation_Nat_C128HR function may be used as a calculated field. For example:
IDAutomation_Nat_C128HR( "~202" & GS1DataField )
- A
GS1 MOD10
check digit may also be calculated within the barcode. For example, a GS1-128 symbol with
17 digits of numbers in the GS1DataField
field could be created with the following formula:
IDAutomation_Nat_C128( "~202" & GS1DataField & "~m17" )
Additionally, the HR field may also be created:
IDAutomation_Nat_C128HR( "~202" & GS1DataField & "~m17" )
Functions of the Linear Barcode Generator
DataToEncode is the only required parameter in the functions provided. Optional parameters are separated with the pipe "|" character and may be appended to the DataToEncode, for example, IDAutomation_Nat_C39("TESTDATA" & "|3" ; 8)
| Linear Barcode Custom Functions |
| IDAutomation_Nat_C128 (DataToEncode | optional ApplyTilde ; BarHeight) |
| IDAutomation_Nat_C128a (DataToEncode ; BarHeight) |
| IDAutomation_Nat_C128b (DataToEncode ; BarHeight) |
| IDAutomation_Nat_C128c (DataToEncode ; BarHeight) |
| IDAutomation_Nat_C39 (DataToEncode | optional N_Dimension ; BarHeight) |
|
IDAutomation_Nat_C39M43 (DataToEncode | optional
N_Dimension ; BarHeight) This function is Code 39 with the check digit included. |
| IDAutomation_Nat_C93 (DataToEncode ; BarHeight) |
| IDAutomation_Nat_Codabar (DataToEncode | optional N_Dimension | optional startchar | optional stopchar ; BarHeight) |
| IDAutomation_Nat_I2of5 (DataToEncode | optional N_Dimension ; BarHeight) |
|
IDAutomation_Nat_I2of5M10 (DataToEncode | optional
N_Dimension ; BarHeight) This function is ITF with the check digit included. |
| IDAutomation_Nat_MSI (DataToEncode | optional N_Dimension | optional IncludeCheckDigit ; BarHeight) |
Description of the Properties of the Functions:
- DataToEncode
This is a string value that represents the data being encoded. - BarHeight
The height of the barcode. The recommended default is 8. The approximate height is determined with the following formula:
Height in Inches = (Font Size) * (BarHeight) * 0.012
Height in CM = (Font Size) * (BarHeight) * 0.03 - N_Dimension
Determines the width of the wide bars, which is a multiple of the X dimension. Valid values are 2 and 3. The default is 2. - IncludeCheckDigit
Determines whether a check digit should be automatically calculated and included for the DataToEncode. Valid values are 0 (false) and 1 (true). Default = 0 for Code 39 and Interleaved 2 of 5. - ApplyTilde
If ApplyTilde is set to 1 (true), the default value, the tilde will be processed. Set this to 0 (False) to disable this feature.
Technical Support
Priority phone, email, and forum support are provided up to 30 days after purchase. Additional priority phone, email, and forum support may be obtained if the Priority Support and Upgrade Subscription is active.
Common Problems and Solutions:
- If the barcode is truncated, looks corrupted, or does not appear completely, resize or increase the width of the field.

- If the resulting symbol contains boxes instead of a barcode,
it is because the process used does not completely support Unicode characters.
Usually, this is caused by processes that create PDF documents.

- If horizontal lines appear in the printed barcode, check
the text format and decrease the Line
Spacing Height to 0.95 or less. However, it is normal for
horizontal lines to appear on the screen because of the low screen resolution.
- If the barcode field is empty, ensure all functions are imported from the database as described in step 4.
- If scanning problems are encountered with small barcode sizes,
verify a printer of 300 DPI or greater is being used. An X dimension
of 16 MILS or greater should be used with low-resolution thermal 203
DPI printers. IDAutomation also offers many barcode fonts that
print well
to low-resolution thermal printers. Additionally, verify the scanner being used can read small barcodes.
- If barcodes do not scan at the default settings, check to
make sure that the barcode type is enabled in the scanner and that there
is sufficient white space surrounding the barcode. Additional solutions
are provided in the
Barcode will not
scan KB article.
- Additional problems and solutions are provided at IDAutomation's barcode font troubleshooting site and by searching resolved public forum threads.

